Understanding Chronic Inflammation: The Hidden Health Threat
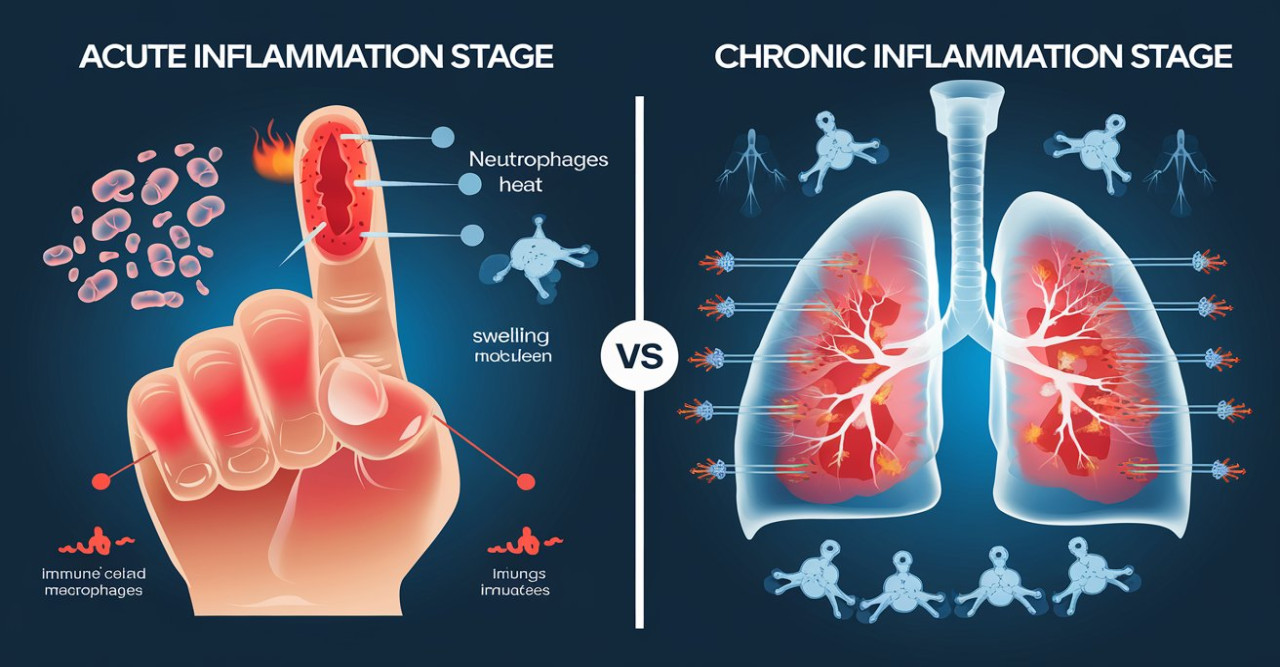
Inflammation is a fundamental physiological response to injury and disease. It is a complex process involving a number of immune cells, signaling molecules, and blood vessels that coordinate to repair damaged tissue and repel pathogens. Acute inflammation is the body's immediate response to injury and generally subsides when the threat has passed. However, problems arise when inflammation is prolonged, persisting far longer than the insult or injury is present. Such a prolonged state has profound health consequences, making it increasingly scientifically interesting.
Health Related News
What Is Chronic Inflammation?
Chronic inflammation is a long-term immune response that could be several months or even years long. On the contrary, chronic inflammation does not leave any symptom like redness of the skin with heat and swelling, besides pain that is felt as a sign of inflammation where the disease has occurred. The tissues remain in such a hyperimmune state resulting in damages to the originally healthy tissues. It still remains unclear why some humans develop chronic inflammation while other humans do not. This condition is very complex and involves genetics, environmental influences, and lifestyle choices.
The Role of Inflammation in Disease
According to research findings, chronic inflammation has been related to major health problems. The professor at Newcastle University in the UK said that chronic inflammation is a driving force for most common diseases. This includes cardiovascular diseases, for instance, heart attacks and strokes. The resulting inflammation can lead to arteries being clogged with plaque and build-up, thereby increasing the risk of cardiovascular events.
Chronic inflammation has also been implicated as a cause in the development of cancer. The persistent immune response will damage DNA, which is a precursor to mutations causing cancerous growth. Chronic types of inflammation are also related to the development of particular cancers, such as inflammatory bowel disease that can increase the risks of colon cancer.
Arthritis is another disease marked by inflammation of the joints. This disease is a painful condition with swelling of the joints and destruction caused to the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune response due to which the immune system works against the tissues in the joints. Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and other types of dementias, also feature chronic inflammation. In these diseases, chronic inflammatory processes may contribute to the death of neurons as well as the accumulation of toxic proteins in the brain.
Besides the physical health consequences, chronic inflammation is now considered to have a role in the causation of mental health conditions. Recent findings point to that individuals suffering from depression and anxiety have an increase of inflammatory markers within the bloodstream. Such association of the immune system with the psychology sparks the question on whether chronic inflammation may also be influential in general wellbeing.
Determination of Chronic Inflammation
Usually, chronic inflammation can be easily detected through blood tests where specific chemical markers are measured. Such markers include CRP and various cytokines that may give an indication of the inflammation level in the body. High levels of such markers may suggest the possibility of an on-going inflammatory process and may warrant further investigation.
The identification of chronic inflammation is important because it serves as an early warning of the onset of several diseases. With such recognition of the presence of chronic inflammation, healthcare providers can start their intervention processes sooner before such diseases are advanced further. Lifestyle modification, medicines, and other interventions would manage inflammation to prevent many of the problems that will accompany it.
Causes of Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation results from the complex interplay of several factors, and in order to provide proper prevention and treatment, these need to be understood and targeted. A genetic predisposition may exist; for example, patients who have a history of inflammatory diseases in the family may be at risk. Exposure to pollution, toxins, and pathogens is equally important as environmental factors causing or aggravating inflammatory reactions.
Lifestyle factors greatly influence inflammation. Diet, exercise, stress, and sleep are all major contributors to the inflammatory state of the body. High intake of processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats tend to increase inflammation, while anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, decrease it. It has been proven that exercise is anti-inflammatory, and chronic stress is pro-inflammatory, so stress management should be an important part of one's health.
Association with Chronic Inflammation of the Process of Ageing
The age-related chronic inflammation hypothesis has recently been proposed by the idea that perhaps the ageing process itself may be driven by inflammation. It has been termed "inflammageing", with a description of inflammatory marker accumulation as a human being ages. The aging body is characterized by senescent cells, those which cease the cycle of division but retain metabolic activity. These senescent cells can elaborate inflammatory substances in favor of a chronic inflammatory state and have even been suggested to drive a more accelerated aging process.
This relationship represents how anti-inflammatory treatments would prevent the disease occurrence first and ensure healthy ageing besides. Anti-inflammatory treatment within chronic inflammation could potentially maximize their quality of life at certain times with ageing; their onset delays various diseases, relating to old ages.
Conclusion
Chronic inflammation can explain almost all the ordinary diseases and conditions. This process needs to have an understanding of its mechanism, its presence, and the treatment of its risk factor. Healthy lifestyles and information about signs of chronic inflammation can equip people with the capacities to take preventive measures within themselves and even add years onto their lives. As the study becomes more revealing about inflammation intricacies, it seems clearer that this fundamental biological reaction is the door to much regarding health and disease.




.jpg)





.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)
-(1).jpg)




.jpg)


